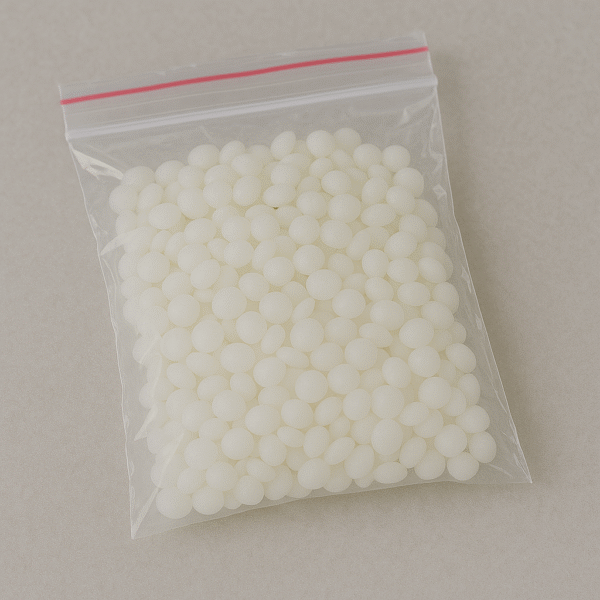
White beeswax is virtually identical to natural yellow beeswax, differing only in color. It is bleached to meet requirements where a yellow tint is undesirable.
Beeswax functions as an emulsifier and provides body and firmness to lotions, creams, and body butters. In soap, it enhances hardness and longevity, while in lip balms it contributes structure and stability. Beeswax is also widely used in candles, since it burns cleaner and longer than petroleum-based waxes.
In cosmetic formulations, beeswax imparts viscosity, delivers nurturing care properties, and ensures good adhesion to the skin. It also acts as a stabilizer in pastes and ointments.
Features:
-
Builds stable emulsions and improves water-binding capacity in ointments and creams.
-
Forms a protective, non-occlusive layer on the skin, enhancing the action of sun creams. It improves elasticity and plasticity, allows the formation of thinner films, and increases durability on skin and lips.
-
Improves soap performance by forming a protective film on the skin and enhancing elasticity.
-
Enhances the protective effect of sun creams and is well tolerated, with a low risk of allergic reactions.
-
Delivers desired effects even at low concentrations, typically 1 to 3 percent.
-
Improves the appearance, consistency, and stability of creams and lotions.
-
A preferred ingredient in lipsticks, where it contributes to sheen, texture, and color stabilization.
Beeswax is considered safe for human consumption and is listed as an authorized food additive under EU food regulations. It is inert, meaning it does not interact with the digestive system and passes through the body unaltered. Substances dissolved or encapsulated in wax are released gradually, and this property is widely applied in medicinal preparations.